Main activities and results 2017
WP 2: Functionalization of the 3D metallic nanofoams
Task 2.2 – Functional electrodes for hydrogen production Objective: surface functionalization for H2 production through: (i) deposition of Pd /Pt clusters by electroless or electrochemical routes onto Ni and Ni alloy foams; (ii) formation of porous Ni(OH)2 surfaces by oxidising the metallic Ni foams structures; (iii) formation of polpyrrole (PPy) clustered films onto the Ni and Ni alloys foams
Pd/Pt surface functionalisation of porous Ni and Ni-Mo alloy structures
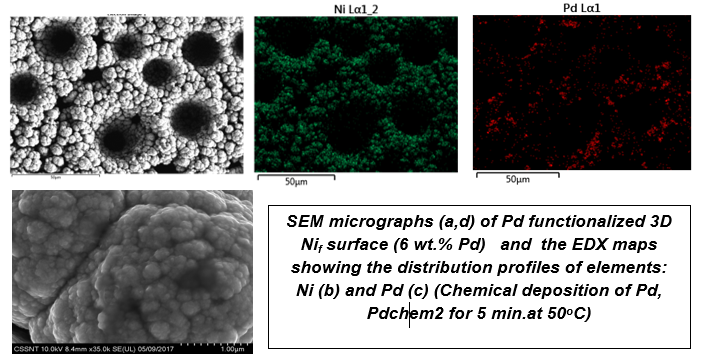
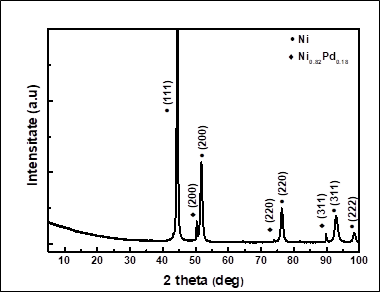
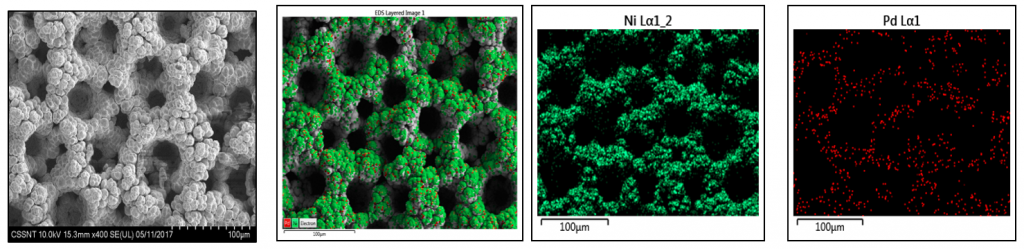
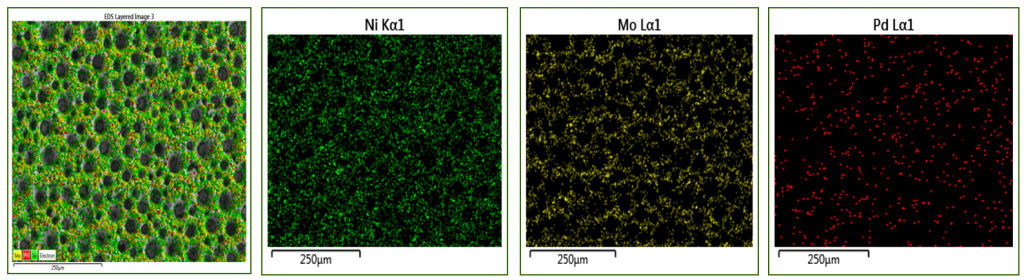
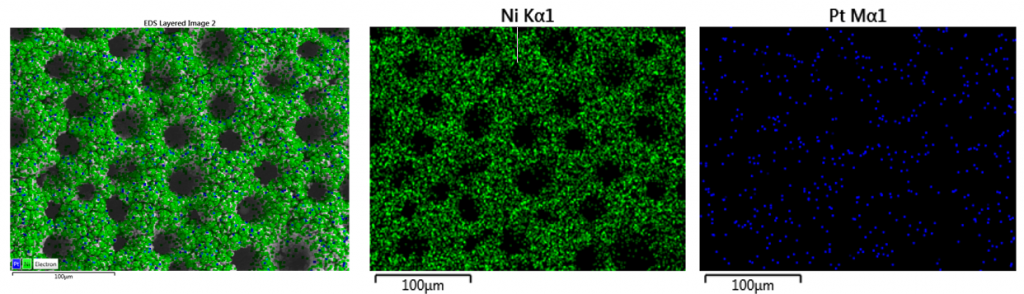
| The addition of PdCl2 in the electroforming electrolyte facilitates the co-deposition of Pd, while keeping the porous morphology of genuine Ni foam. Pd element is quite uniformly distributed within the alloy deposit. Usually the Pd content was in the range of 0.3-3 wt.% with higher values on the increase of Pd concentration in the electrolyte or of the applied current density. |
(0.5 % Pd) at 60oC for 20 min. (c.d = 4 A/dm2)
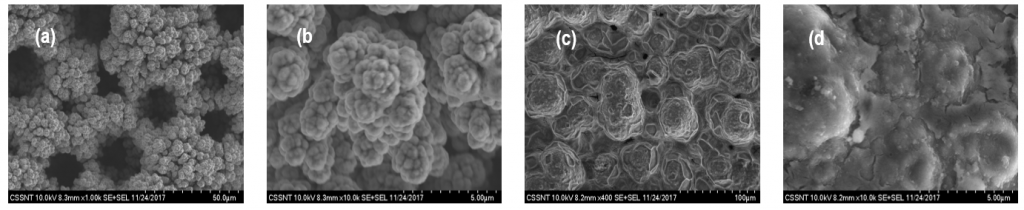
Formation of porous Ni(OH)2 surfaces

Formation of polpyrrole (PPy) clustered films onto the Ni and Ni alloys foams
WP 5 – Electrochemical performance of metallic nanofoams as electrodes for hydrogen production
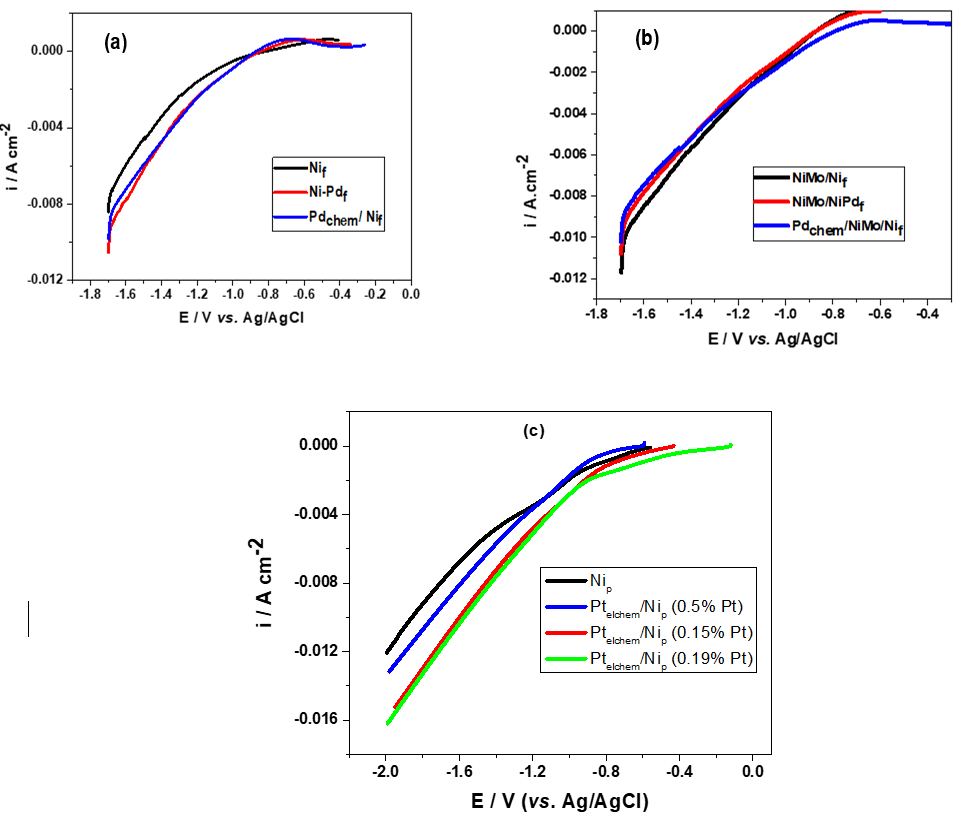
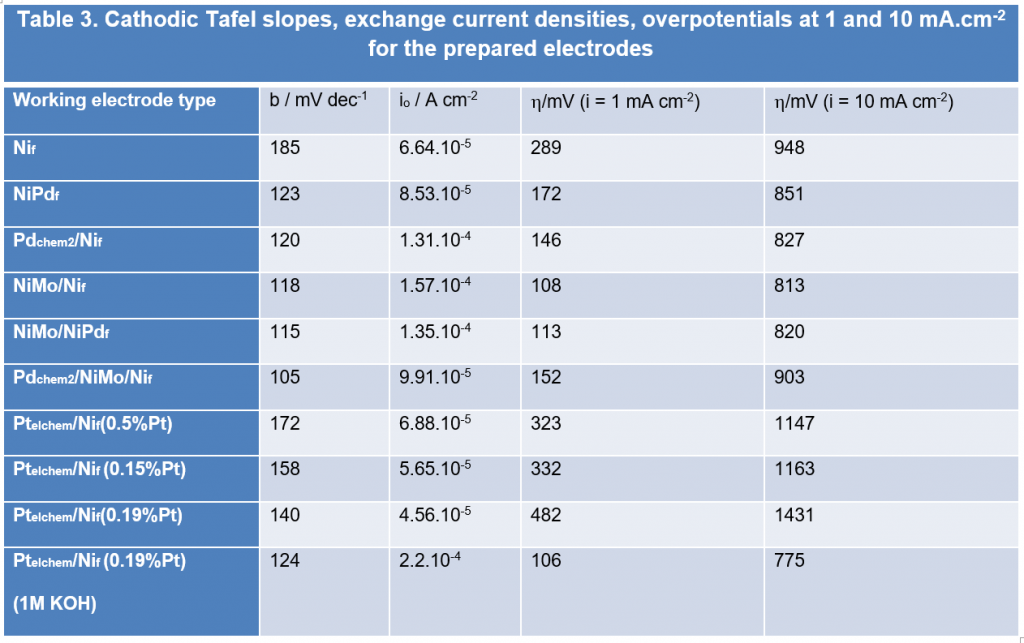
The HER activity of Nif may be enhanced through Pd surface modification. The corresponding Tafel slopes for NiPdf and Pdchem/Nif are of 123 and 120 mV.dec-1, respectively, suggesting that the HER process obeys Volmer reaction mechanism. The higher value of Nif may be related to the presence of oxides films on the surface. The Pd functionalization of Ni-Mo alloy based systems determines only a slight improvement of the catalytic activity. The significant effect is mainly due to the presence of Mo as alloying element. The determined Tafel slope values ranged from 118 to 105 mV.dec-1, indicating the Volmer step as rate determining step.
Pt surface modification provides moderate performance against HER as compared to Pd in the case of seawater electrolyte. However Pt improved the HER activity when 1M KOH alkaline electrolyte has been involved, materialized by exchange current values of one order of magnitude higher.